Does a water molecule become more or less polar when bound to a metal ion, such as 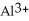 ? Why? (Hint: How might the electrons of the O-H covalent bonds in water "feel" about the highly charged aluminum ion?)
? Why? (Hint: How might the electrons of the O-H covalent bonds in water "feel" about the highly charged aluminum ion?)
Definitions:
Risk Management
The process of identifying, assessing, and prioritizing risks followed by coordinated efforts to minimize, monitor, and control the probability or impact of unfortunate events.
Insurance Company
An entity that provides financial compensation to individuals or entities against losses from specified risks in exchange for premiums.
Risk Distribution
The practice of spreading financial risk across various parties, investments, or financial instruments to reduce the impact of any one failure.
Age Misrepresentation
The act of deliberately falsifying one's age, usually for the purpose of gaining access to certain privileges or avoiding restrictions.
Q3: Which of the following would cause the
Q20: The main role of DNA is to
Q30: Why is it easier for the body
Q35: Alkaloid salts are not very soluble in
Q60: Why can't your body produce proteins from
Q87: Which of the following statements about strong
Q100: Two amu equals how many grams? (1
Q107: Shown below is the line structure of
Q110: Why does adding heat to ice-water disfavor
Q143: There are 1000 liters in 1 cubic