Below is the narrative of the "Manage customer accounts" portion of the B/AR/CR process.Narrative Description
Processes 2.1 through 2.3 relate to sales returns adjustments.This process begins when there is notification from the receiving department that goods have been returned by a customer.Subprocess 2.1 obtains data from the accounts receivable master data to validate the return.If the sales return is not valid, it will be rejected (see Reject stub) and processed through a separate exception routine.If the sales return is valid, it is sent to subprocess 2.2 where a credit memo is prepared and sent to the customer, and the accounts receivable master data is updated to reflect the credit.At the same time, the
validated sales return is sent to subprocess 2.3 where a journal voucher is prepared, which is used to create a record in the AR adjustments event data store (i.e., the journal), and the general ledger is notified that a credit memo has been issued.This results in updates to sales returns and allowances and to AR.Process 2.4 is triggered by a periodic review of aging details obtained from the accounts receivable master data.This report would be used to identify and follow up on late-paying customer accounts.One of two types of adjustments might result from this review:
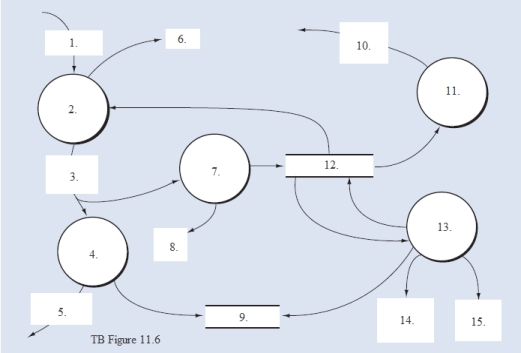
-The recurring adjusting entry for estimated bad debts.-The periodic write-off of "definitely worthless" customer accounts.Like process 2.4, bubble 2.5, "Prepare customer statements," also is triggered by a periodic event that recurs at specified intervals, often on a monthly basis in practice.Details of unpaid invoices are extracted from the accounts receivable master data and are summarized in a statement of account that is mailed (or sent electronically) to customers.Required: From the DFD in TB Figure 11.5 and the narrative description above, explode bubble 2.0 into a lower-level diagram showing the details of that process by identifying the words that belong in items 1.to 15.(TB Figure 11.6). 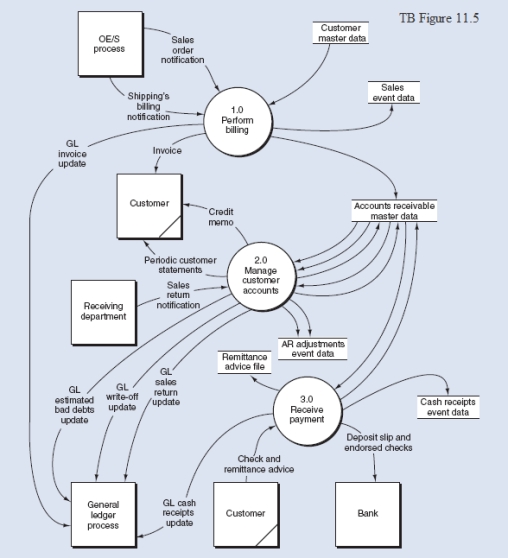
Definitions:
Productivity Measurement
The evaluation of the efficiency of a worker, machine, or system in converting inputs into useful outputs.
Evaluation System
A formal process used to assess the performance, effectiveness, or value of individuals, projects, or programs.
ProMES
A performance management system that focuses on measuring and improving job performance through specific goals and feedback.
Job Characteristics Approach
A theory that suggests jobs can be designed to enhance employee motivation, satisfaction, and performance by focusing on five core job dimensions.
Q4: Trends in cost management/cost accounting include all
Q7: Which batch control total generally has no
Q44: The trigger for the payroll process "pay
Q78: For payment voucher input validity, which control
Q90: The _ covers the progression of information
Q96: The first list below contains 10 control
Q118: The control environment reflects the organization's general
Q125: In a B/AR/CR process, which of the
Q132: Computer software that is used to facilitate
Q143: _ is a process that assesses the