The amount of money that Jon can save after working for a summer is a random variable S with a mean of 
And a standard deviation of 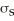
.After saving this money Jon plans to go on a trip to India.He will change his money into Rupees at an exchange rate of 43 Rupees to one Dollar.This money he will bring to India.When he arrives in India he will buy a used motorbike.The price in India of a motorbike of the type he wants is a random variable B with a mean of 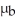
Rupees and a standard deviation of 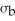
Rupees .
The amount of money Jon will have left (in Rupees) after changing his savings into Rupees and buying a motorbike in India is a random variable P which can be expressed in terms of S and B as P = 43S - B.
Find expressions for the mean and variance of the random variable P.Assume that Jon's savings and the price of the bike are independent.
Definitions:
Electoral College
A body of electors established by the United States Constitution, responsible for electing the president and vice president based on the popular vote in each state.
Majority Totals
The amount or number required to surpass half of a total count, especially in the context of votes or decisions.
Ideological Platforms
Ideological platforms are the sets of beliefs, values, and policy principles that political parties, candidates, or movements adopt and promote to distinguish themselves and to guide their political and legislative actions.
Q1: On a multiple choice test with 15
Q2: You pick a card from a deck.If
Q22: In City A,7420 people are unemployed in
Q25: How much fat do reduced fat cookies
Q28: Roll a die and record the number.Then
Q32: We draw a card from a deck
Q58: In a language program at a university,14%
Q72: In the past,the mean battery life for
Q78: The amount of money that Maria earns
Q109: At a furniture factory,tables must be assembled,finished,and