The functional groups in the aspirin molecule shown are 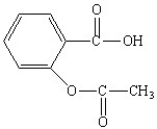
Definitions:
Unreasonable Risk
A level of danger that surpasses what is considered acceptable or safe in a given context.
Comparative Negligence
A legal doctrine that allocates damages based on the degree of fault of each party involved in an accident.
Contributory Negligence
A legal doctrine stating that if the plaintiff in a tort law case is found to be partially at fault for the accident, they may be barred from receiving compensation.
Unfounded Claims
Assertions or allegations that lack supporting evidence or basis in fact, often considered to be baseless or false.
Q9: Protein denaturation results in a disruption of
Q16: In the molecule 3,3-dimethylhexane,carbon number two is<br>A)primary.<br>B)secondary.<br>C)tertiary.<br>D)quaternary.<br>E)none
Q29: When 2-butene reacts completely with bromine,the product
Q34: Compounds of the type R<sub>3</sub>C-OH are referred
Q37: Which of the following molecules contains both
Q49: The carbon skeleton of an alkane is
Q58: stable isotopes<br>A)a unit of measurement of radiation
Q81: Nylons and proteins are both referred to
Q82: Myoglobin is a protein that contains oxygen
Q86: When hydrocarbons undergo complete combustion,the product(s)is(are)<br>A)CO<sub>2</sub> and