A)What is the name of the following disaccharide?
B) What two monosaccharides compose it?
C) What type of glycosidic linkage is between the two?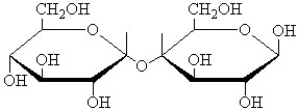
Definitions:
Association Areas
Regions of the brain that integrate information from various parts of the brain to perform more complex functions, including reasoning, problem-solving, and interpreting sensory information.
Sensory Information
Data received by the sensory organs (eyes, ears, skin, tongue, and nose), which is then interpreted by the brain.
Corpus Callosum
A wide bundle of nerve fibers linking the brain's two halves, enabling communication between hemispheres.
Neural Fibers
Long, slender projections of nerve cells, or neurons, that conduct electrical impulses away from the neuron's cell body.
Q2: Mutarotation is process where<br>A)glucose undergoes reaction to
Q10: Digestion of lipids begins in the _,in
Q11: Ketogenic amino acids cannot be converted into
Q12: Reaction of an ester with a strong
Q18: Reduction of aldehydes and ketones is a<br>A)one-step
Q26: According to the current working draft of
Q37: Which of the following monosaccharides is present
Q42: The isoelectric point of an amino acid
Q80: When a molecule other than the correct
Q88: Which molecule is an amide?<br>A)<br><img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4943/.jpg" alt="Which