The view in the figure is from above a plane mirror suspended by a thread connected to the center of the mirror at point C. A scale is located 0.65 m (the distance from point C to point A) to the right of the center of the mirror. Initially, the plane of the mirror is parallel to the side of the scale; and the angle of incidence of a light ray which is directed at the center of the mirror is 30°. A small torque applied to the thread causes the mirror to turn 12° away from its initial position. The reflected ray then intersects the scale at point B. What is the distance from point A to point B on the scale? 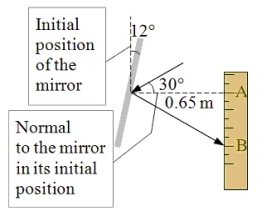
Definitions:
Standard Errors
The standard deviation of the sampling distribution of a statistic, commonly used in estimating the margin of error.
Operating Characteristic Curve
A graph that shows the capability of a test to distinguish between different states, such as defective and non-defective items.
Type II Error
The statistical mistake of failing to reject a false null hypothesis, or the error of not detecting an effect or difference when one truly exists.
Type I Error
Incorrectly dismissing a true null hypothesis as false.
Q6: What is the magnitude of the magnetic
Q11: Which one of the following statements concerning
Q15: A long, straight wire is in the
Q28: How much energy is dissipated in
Q32: Three parallel plate capacitors, each having
Q36: Makenzie walks directly toward a plane mirror
Q47: Determine the energy of the photon emitted
Q51: A camera with a focal length of
Q54: Note the different types of electromagnetic radiation:
Q101: Jarmon Company owns twenty-three percent (23%) of