The figure shows a circuit. The switch S can be closed on either point A or C, but not both at the same time. Use the following quantities:
V1 = V2 = 12 V
R1 = R4 = 1.0
R2 = R3 = 2.0 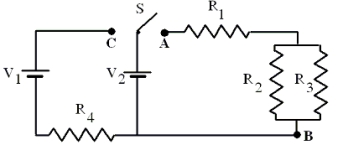
-What is the equivalent resistance between the points A and B?
Definitions:
Price Elasticity
Price elasticity measures how the quantity demanded or supplied of a good changes in response to a change in its price.
Linear Demand
A type of demand relationship where changes in price lead to direct, proportional changes in quantity demanded.
Price Elastic
An assessment of the influence that price changes have on the consumer's purchasing volume of a good.
Inversely Related
A relationship between two variables where one increases as the other decreases.
Q5: Which one of the following will result
Q8: A 3.0-A current is maintained in
Q19: Determine the rms current through this element.<br>A)1.4
Q23: Determine the induced emf in the loop.<br>A)0.7
Q26: When a light bulb is connected
Q31: An ideal gas is contained in a
Q33: What is the temperature of the gas
Q36: What is the rms value of the
Q36: Light emerges from a polarizer that has
Q54: Note the different types of electromagnetic radiation: