A 200.0-kg object is attached via an ideal pulley system to paddle wheels that are submerged in 0.480 kg of glycerin at 20.0 °C in an insulated container as shown. Then, the object falls through a distance of 5.00 m causing the paddle wheel to turn. Assuming all of the mechanical energy lost by the falling object goes into the water, determine the final temperature of the glycerin. The specific heat capacity of glycerin is 2410 J/ 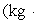 Co) .
Co) . 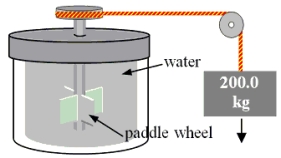
Definitions:
REM Rebound
The phenomenon where there is an increase in the amount of REM (Rapid Eye Movement) sleep after a period of REM sleep deprivation.
Slow-Wave Sleep
The deepest phase of non-REM sleep, characterized by slow brain waves, reduced heart rate, and deep physical relaxation, which is restorative and vital for memory consolidation.
Bed-Wetting
Involuntary urination while asleep, especially common in children.
Sleep Spindles
A burst of oscillatory brain activity visible on an EEG that occurs during stage 2 of non-REM sleep.
Q11: A flask contains 1.00 mole of oxygen
Q15: Determine the power dissipated by the
Q16: A capacitor is initially charged to 3
Q36: Will the balloon rise, fall, or remain
Q41: A paddle wheel frictionally adds thermal energy
Q44: An ice cube, <span class="ql-formula"
Q46: A bicycle travels 141 m along a
Q49: What is the current through the resistor
Q52: Neon is a monatomic gas with a
Q69: Under which one of the following conditions