. The figure shows the free-body diagram for the block. 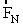 represents the normal force on the block; and
represents the normal force on the block; and 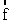 represents the force of kinetic friction.
represents the force of kinetic friction. 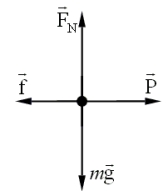
-If the coefficient of kinetic friction, 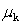 , between the block and the surface is 0.30 and the magnitude of the frictional force is 80.0 N, what is the weight of the block?
, between the block and the surface is 0.30 and the magnitude of the frictional force is 80.0 N, what is the weight of the block?
Definitions:
Barbiturates
A class of drugs historically used for their sedative, hypnotic, and anxiolytic properties, though now less common due to the risk of dependence and overdose.
Amphetamines
A class of psychoactive drugs that stimulate the central nervous system, increasing energy and alertness.
Barbiturates
A class of drugs that act as central nervous system depressants, often used for their sedative and anxiolytic effects.
Hallucinogens
A category of drugs that can alter and distort perceptions of time and space, alter mood, produce feelings of unreality, and cause hallucinations; also called psychedelics.
Q2: Which one of the following statements best
Q3: Town A lies 20 km north of
Q12: They are learning to document sources while
Q12: The professor was surprised that four _
Q22: The cheerful sounds <span class="ql-formula"
Q35: A 71-kg man stands on a bathroom
Q45: What is their combined angular momentum about
Q71: Which one of the following statements concerning
Q82: Which statement accurately describes the motion of
Q195: The main reason for our balance of