A block is at rest on a rough inclined plane and is connected to an object with the same mass as shown. The rope may be considered massless; and the pulley may be considered frictionless. The coefficient of static friction between the block and the plane is μs; and the coefficient of kinetic friction is μk. 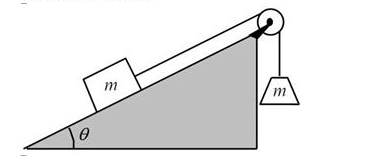
-If the rope were cut between the block and the pulley, what would be the magnitude of the acceleration of the block down the plane?
Definitions:
Average Service Rate
The average number of customers or units that can be processed over a certain time frame in a service system.
Expected to Stay
An estimation of the duration or likelihood that an individual or item remains in a particular state or location.
M/D/1
M/D/1 is a queueing model designation indicating a system with a Poisson arrival process (M), deterministic service times (D), a single server (1), and exponential service times.
Constant Service Time
A situation where the time required to serve a customer or complete a process is the same each time, allowing for predictable scheduling and planning.
Q3: A 2150-kg truck is traveling along a
Q3: My brother is a <span
Q10: Each entrant must have _ identification checked..<br>A)his<br>B)her<br>C)their<br>D)his
Q10: A 1500-kg satellite orbits a planet in
Q16: A 14-kg beam is hinged at one
Q18: A circular disk of radius 0.015 m
Q24: A string is tied to a doorknob
Q36: To sustain good health, _ important to
Q39: In an amusement park ride, a child
Q85: A 2.0-N rock slides on a