A vector 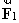 has a magnitude of 40.0 units and points 35.0° above the positive x axis. A second vector
has a magnitude of 40.0 units and points 35.0° above the positive x axis. A second vector 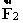 has a magnitude of 65.0 units and points in the negative x direction. Use the component method of vector addition to find the magnitude and direction, relative to the positive x axis, of the resultant
has a magnitude of 65.0 units and points in the negative x direction. Use the component method of vector addition to find the magnitude and direction, relative to the positive x axis, of the resultant 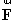 =
= 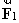 +
+ 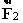 .
.
Definitions:
Marginal Cost
The cost of producing one additional unit of a product or service, an important concept in economics for decision-making regarding production levels.
Total Variable Costs
The sum of all costs that vary with the level of output, including materials, labor, and other expenses that increase or decrease as production changes.
Natural Monopoly
A market condition where due to high fixed costs or unique resources, a single company can supply a product or service at a lower cost than any potential competitor, thus dominating the market.
Unit Costs
The price a business incurs for the production, storage, and distribution of a single unit of a certain product or service.
Q23: If nations trade on the basis of
Q24: The limping grizzly bear evidently had hurt
Q30: A Canadian goose flew 845 km from
Q44: Nations which experience relatively high rates of
Q47: A top fuel dragster with a mass
Q48: Complete the following statement: The ratio <img
Q62: Determine the magnitude of the acceleration of
Q74: The book has an acceleration of 0
Q115: In 2009, we ran a _ on
Q150: If the dollar depreciates in value against