A particular first-order reaction has a rate constant of 1.35 × 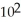
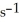 at 25.0 °C.What is the magnitude of k at
at 25.0 °C.What is the magnitude of k at 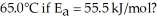
Definitions:
Unborn Children
Refers to fetuses or embryos that are in the developmental stages within the womb, prior to birth.
Prenatal Development
The process of growth and development inside the womb, from conception to birth, encompassing all phases of embryonic and fetal development.
Zygote
The initial cell formed when a new organism is conceived, resulting from the union of an ovum and a sperm cell.
Fetus
A developmental stage of a vertebrate that occurs in the womb after embryonic stage and until birth.
Q2: What type(s)of intermolecular forces exist between NH<sub>3</sub>
Q2: The elementary reaction 2NO<sub>2</sub> (g)→ 2NO (g)+
Q15: At elevated temperatures,dinitrogen pentoxide decomposes to nitrogen
Q23: In a saturated solution of a salt
Q32: In the presence of oxygen,the nitrogen present
Q35: Which of the following statements is false?<br>A)The
Q46: What is the predominant intermolecular force in
Q52: What is/are the product(s)of photodissociation of molecular
Q69: In general,as activation energy increases,reaction rate _.<br>A)goes
Q98: The concentration of fluoride ions in a