Annual Compounding. The following table shows annual sales data for Stuff Happens, Inc., over the ten-year 1998-2008 period:
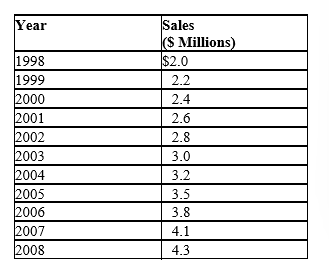
A. Calculate the 1998-2008 growth rate in sales using the constant rate of change model with annual compounding.
B. Forecast sales for the years 2011 and 2013.
Definitions:
Net Income
The total profit of a company after accounting for all costs and expenses, including taxes and operational expenses.
Accrued Revenues
Revenues that have been earned but not yet received in cash or recorded at the statement date.
Accounting Period
A specific period of time for which financial accounts are prepared, commonly a year or a quarter.
Salaries Expense
Represents the total amount paid to employees as wages or salaries before any deductions, recognized in the accounting period in which employees' services are utilized.
Q9: Utility is measured by:<br>A) wealth.<br>B) price.<br>C) value
Q12: Marginal revenue product equals:<br>A) marginal revenue multiplied
Q20: Optimal Price. Last week, Discount Food Stores,
Q20: Diversifying among different suppliers is an example
Q22: <br>A. Demand estimation is made difficult by
Q30: A product that enjoys rapidly growing demand
Q35: The production function Q = 0.25X<sup>0.5</sup>Y exhibits:<br>A)
Q43: Granny's Jug Herbal Shop has total current
Q45: Expected Return Analysis. Barry Bonds offers free
Q62: What was the free cash flow in