Secure Strategies. Suppose two competitors, McGraw-Hill, Inc., and Pearson, PLC., each face an important strategic decision concerning whether or not they should boost promotion on new product introductions. McGraw-Hill can choose either row in the payoff matrix defined below, whereas Pearson can choose either column. For McGraw-Hill, the choice is either "boost promotion" or "hold promotion constant." For Pearson, the choices are the same. Notice that neither firm can unilaterally choose a given cell in the profit payoff matrix. The ultimate result of this one-shot, simultaneous-move game depends upon the choices made by both competitors. In this payoff matrix, the first number in each cell is the profit payoff to McGraw-Hill; the second number is the profit payoff to Pearson (in billions).

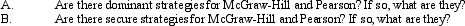
Definitions:
Qualitative Models
Approaches in research and analysis that focus on the qualities, characteristics, and meanings of phenomena rather than numerical data.
Stable Markets
Markets characterized by steady demand, predictable competition, and consistent growth, with minimal fluctuations.
Demand For Labour
The total amount of workers that employers want to hire at a given wage rate and time.
Structural Equation Modelling
A statistical technique that examines complex relationships among variables by testing theoretical models.
Q7: Demand Analysis. The demand for automobiles is
Q12: Profit Probability Estimation. Intimate Lighting, Inc., is
Q17: External Social Benefits. During recent years, professional
Q18: Managers who seek satisfactory rather than optimal
Q24: Expected Return. Pediatric Medicine, Ltd., is considering
Q25: Monopoly profits reflect:<br>A) competitive advantage.<br>B) comparative advantage.<br>C)
Q27: Price/Output Determination. Orange Freight, Inc., an over-the-road
Q30: A product that enjoys rapidly growing demand
Q32: Cartel Pricing. The domestic color separator manufacturing
Q34: Regression Statistics. Financial Planning Associates, Ltd., has