Secure Strategies. Suppose two competitors, McGraw-Hill, Inc., and Pearson, PLC., each face an important strategic decision concerning whether or not they should boost promotion on new product introductions. McGraw-Hill can choose either row in the payoff matrix defined below, whereas Pearson can choose either column. For McGraw-Hill, the choice is either "boost promotion" or "hold promotion constant." For Pearson, the choices are the same. Notice that neither firm can unilaterally choose a given cell in the profit payoff matrix. The ultimate result of this one-shot, simultaneous-move game depends upon the choices made by both competitors. In this payoff matrix, the first number in each cell is the profit payoff to McGraw-Hill; the second number is the profit payoff to Pearson (in billions).

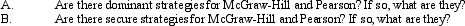
Definitions:
Motivation
The inner drive or process that stimulates and directs human behavior towards achieving goals.
Amount Of Information
The volume or quantity of data and knowledge accessible or required to make informed decisions.
Internal Versus External
A comparison between factors that are inside (internal) and outside (external) of an individual or entity, which can influence behavior or outcomes.
Clarity
The quality of being easily understood, completely transparent, or clear in thought, expression, or presentation.
Q3: The accumulated earnings credit for a personal
Q4: Since interest and taxes are deductible by
Q8: Profit Maximization: Equations. Dot.com Products, Inc., offers
Q18: Every one-shot game:<br>A) has at least one
Q22: Industry profits can be increased by constraints
Q23: Utility price and profit regulation is designed
Q24: Profit per unit is rising when marginal
Q25: Which of the following is an administrative
Q60: Zircon Corporation donated scientific property worth $350,000
Q70: Which of these notations would appear after