Match each equation (a-f) to its graph (I-VI).
a. 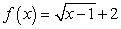 b.
b. 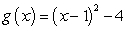 c.
c. 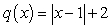 d. r(x) = x + 2 e. h(x) = x3 - 2x2 + 2x - 1 f.
d. r(x) = x + 2 e. h(x) = x3 - 2x2 + 2x - 1 f. 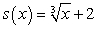 I.
I. 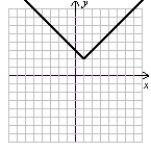 II.
II. 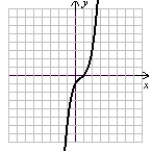 III.
III. 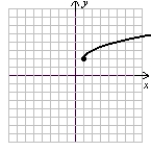 IV.
IV. 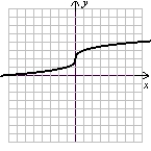 V.
V. 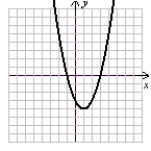 VI.
VI. 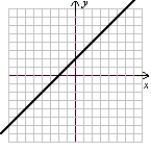 (Gridlines on each graph are spaced one unit apart.)
(Gridlines on each graph are spaced one unit apart.)
Definitions:
Age Stratification
The hierarchical ranking and division of society into groups based on age, affecting access to resources, power, and status.
Class Stratification
The division of society into classes based on wealth, education, occupation, and other social markers, leading to inequality.
Earn Cents
A colloquial expression emphasizing the act of making money, usually in small amounts.
Dollar
The primary currency unit used in the United States, marked by the symbol $ and known as a standard measurement in international financial transactions.
Q14: Use a cofunction identity to write an
Q15: Regarding significant influence with respect to an
Q19: Solve using the zero product property. Be
Q37: Fair value increments on depreciable assets should
Q46: A company is a party to a
Q49: Why are adjustments required for intragroup services
Q54: Use the function value given to
Q62: List all the numbers in the set
Q76: Use the symmetry of the circle and
Q84: Solve using the most efficient method. 4x<sup>2</sup>