The population of a small town can be modeled by the function 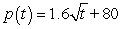 , where p is measured in thousands and t is the number of years after 2008. Find the limit of the difference quotient for p, to obtain a function
, where p is measured in thousands and t is the number of years after 2008. Find the limit of the difference quotient for p, to obtain a function 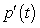 that represents the instantaneous rate of change of population at time t. Use the results to find the instantaneous rate of change of the population of the town in 2024 to the nearest person/yr.
that represents the instantaneous rate of change of population at time t. Use the results to find the instantaneous rate of change of the population of the town in 2024 to the nearest person/yr.
Definitions:
Varied Vocabulary
The range and diversity of words that an individual knows and uses.
Basic Cognitive Processes
Fundamental mental activities involved in learning, perception, memory, and reasoning, which underpin more complex cognitive functions.
Schooling
refers to the process of formal education typically conducted in schools or educational institutions.
Piaget
A psychologist known for his theory on the cognitive development of children, identifying stages that characterize the evolution of thinking abilities.
Q3: The following shows the temperatures (high,low)and weather
Q7: The percent frequency of a class is
Q11: Identify the graph of the equation using
Q25: Find a<sub>k</sub>.<br>A) a<sub>k</sub> = 7k + 3<br>B)
Q31: The numerical value of the variance<br>A)is always
Q63: Solve the system of equations using Cramer's
Q77: When computing the mean of a
Q85: Sketch the polar graph using an
Q88: If a dime is tossed four times
Q93: Which of the following is not