In a Monte Carlo study, econometricians generate multiple sample regression functions from a known population regression function. For example, the population regression function could be Yi = ?0 + ?1Xi = 100 - 0.5 Xi. The Xs could be generated randomly or, for simplicity, be nonrandom ("fixed over repeated samples"). If we had ten of these Xs, say, and generated twenty Ys, we would obviously always have all observations on a straight line, and the least squares formulae would always return values of 100 and 0.5 numerically. However, if we added an error term, where the errors would be drawn randomly from a normal distribution, say, then the OLS formulae would give us estimates that differed from the population regression function values. Assume you did just that and recorded the values for the slope and the intercept. Then you did the same experiment again (each one of these is called a "replication"). And so forth. After 1,000 replications, you plot the 1,000 intercepts and slopes, and list their summary statistics.
Here are the corresponding graphs: 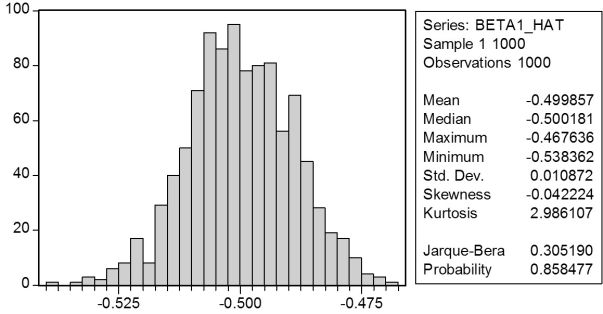
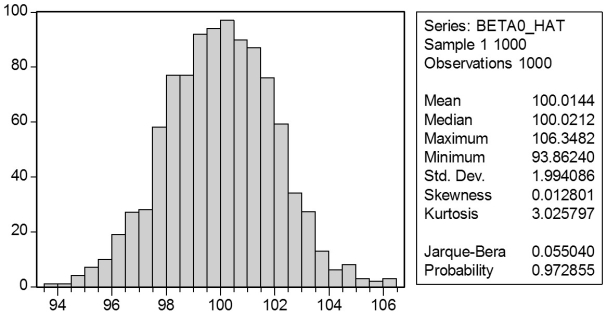 Using the means listed next to the graphs, you see that the averages are not exactly 100 and -0.5. However, they are "close." Test for the difference of these averages from the population values to be statistically significant.
Using the means listed next to the graphs, you see that the averages are not exactly 100 and -0.5. However, they are "close." Test for the difference of these averages from the population values to be statistically significant.
Definitions:
Public Transit
Systems of publicly accessible transportation services intended for general public use, such as buses, trains, and subways.
Antianxiety Drugs
Medications prescribed to alleviate symptoms of anxiety and panic disorders.
Drowsiness
A state of feeling unusually sleepy or tired, often leading to a reduced level of alertness and performance.
Biomedical Therapies
A group of treatments for mental health disorders that involve physiological interventions (such as medication, surgical procedures, or electroconvulsive therapy) to treat symptoms directly related to biological processes.
Q7: Your textbook presented you with the
Q12: An estimator <span class="ql-formula" data-value="\hat
Q16: A statistical analysis is internally valid if<br>A)its
Q18: HAC standard errors and clustered standard errors
Q21: The strong force depends upon the electric
Q28: For W to be an effective control
Q34: SAT scores in Mathematics are normally
Q37: With i.i.d. sampling each of the
Q65: The accompanying table lists the height
Q147: Cold fusion has<br>A)solved the world's energy crisis.<br>B)been