(Continuation of the Purchasing Power Parity question from Chapter 4)The news-magazine The Economist regularly publishes data on the so called Big Mac index and exchange rates between countries. The data for 30 countries from the April 29, 2000 issue is listed below: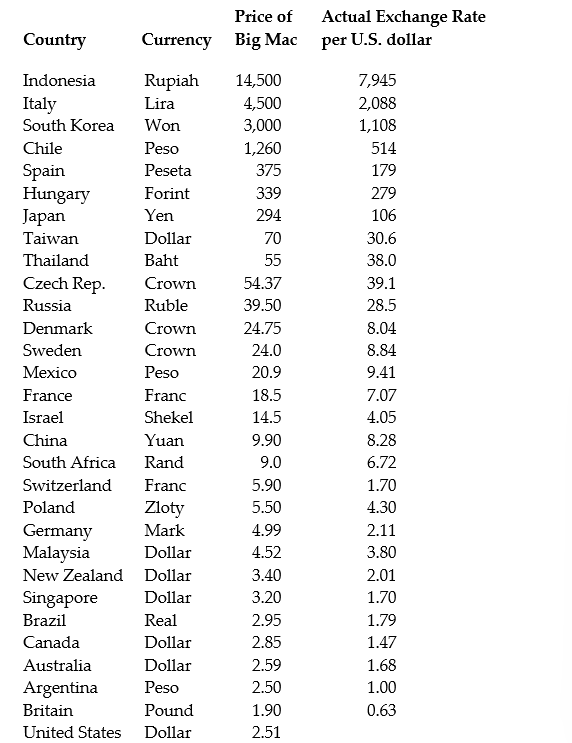
The concept of purchasing power parity or PPP ("the idea that similar foreign and domestic goods … should have the same price in terms of the same currency," Abel, A. and B. Bernanke, Macroeconomics, 4th edition, Boston: Addison Wesley, 476)suggests that the ratio of the Big Mac priced in the local currency to the U.S. dollar price should equal the exchange rate between the two countries.
After entering the data into your spread sheet program, you calculate the predicted exchange rate per U.S. dollar by dividing the price of a Big Mac in local currency by the U.S. price of a Big Mac ($2.51). To test for PPP, you regress the actual exchange rate on the predicted exchange rate.
The estimated regression is as follows: = -27.05 + 1.35 × 1.35×Pr edExRate R2 = 0.994, n = 29, SER = 122.15
(23.74)(0.02)
(a)Your spreadsheet program does not allow you to calculate heteroskedasticity robust standard errors. Instead, the numbers in parenthesis are homoskedasticity only standard errors. State the two null hypothesis under which PPP holds. Should you use a one-tailed or two-tailed alternative hypothesis?
(b)Calculate the two t-statistics.
(c)Using a 5% significance level, what is your decision regarding the null hypothesis given the two t-statistics? What critical values did you use? Are you concerned with the fact that you are testing the two hypothesis sequentially when they are supposed to hold simultaneously?
(d)What assumptions had to be made for you to use Student's t-distribution?
Definitions:
Criminal Lawsuit
A legal proceeding brought against an individual or entity accused of committing a crime, with the intention of achieving a formal judgment of guilt.
Undue Influence
A situation in which an individual is able to exert a level of influence over another person, typically in a way that undermines the individual's free will or judgement, often a concern in contract law and wills.
Concealment
The act of hiding or withholding information, objects, or facts intentionally, often to deceive or gain an unfair advantage.
Nondisclosure
The requirement to keep certain information confidential and not share it without proper authorization or consent.
Q3: What do you do to the control
Q13: One of the least squares assumptions in
Q24: A light year is defined as the
Q30: If the average lifetime of a proton
Q31: In the linear regression model, Y<sub>i</sub> =
Q34: If a 1-kg mass is completely converted
Q39: Consider the time and entity fixed
Q55: Baryon number is conserved in all interactions.
Q61: The color force between quarks is carried
Q62: exploits nuclear fusion<br>A)alpha particle<br>B)atomic bomb<br>C)atomic mass number<br>D)atomic