Table 9.2
A firm has determined its optimal structure which is composed of the following sources and target market value proportions. 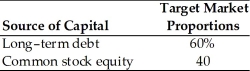 Debt: The firm can sell a 15-year, $1,000 par value, 8 percent bond for $1,050. A flotation cost of 2 percent of the face value would be required in addition to the premium of $50.
Debt: The firm can sell a 15-year, $1,000 par value, 8 percent bond for $1,050. A flotation cost of 2 percent of the face value would be required in addition to the premium of $50.
Common Stock: A firm's common stock is currently selling for $75 per share. The dividend expected to be paid at the end of the coming year is $5. Its dividend payments have been growing at a constant rate for the last five years. Five years ago, the dividend was $3.10. It is expected that to sell, a new common stock issue must be underpriced $2 per share and the firm must pay $1 per share in flotation costs. Additionally, the firm has a marginal tax rate of 40 percent.
-The firm's before-tax cost of debt is ________. (See Table 9.2)
Definitions:
Amide Synthesis
The process of forming amide bonds between carboxylic acids and amines, commonly involving methods such as direct coupling or activation of the carboxylic acid.
Acylation
A chemical process that introduces an acyl group into a compound, often used in organic syntheses to modify molecules.
Amine
An organic compound derived from ammonia (NH3) by replacement of one or more hydrogen atoms by alkyl or aryl groups.
Sodium Methoxide
A chemical compound used as a strong base in organic synthesis, often for the deprotonation of weak acids.
Q5: The conversion feature of a bond is
Q6: Bond indentures include restrictive covenants.These provisions protect
Q15: The portfolio with a standard deviation of
Q20: Unlike creditors,equityholders are owners of the firm.
Q56: In general,net operating losses of a corporation
Q68: Longhorn Partnership reports the following items at
Q83: American Depositary Receipts (ADRs)are claims issued by
Q89: Preferred stock is characterized by _.<br>A)voting rights<br>B)maturity
Q101: Draw a graph of a typical Treasury
Q212: A given change in inflationary expectations will