Compound "K" is the ultimate product of a linear metabolic pathway consisting of ten enzymatically catalyzed reactions as shown below. 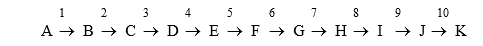
Complete the following description.
If "K" inhibits activity of enzyme "5", then enzyme "5" is under ___ control.If enzyme "3" becomes activated in response to activity of protein kinase A only when compound "A" is present, then enzyme "3" is under ___ control.If enzyme "2" is only expressed in the presence of high concentrations of "A," then enzyme "2" is under ___ control.If all of these are true, high concentrations of "__" will decrease the flux through the pathway.
Definitions:
Organism's Life Cycle
The sequence of biological events and processes that an organism undergoes from its birth until it reproduces offspring.
Heat-Shock Genes
Genes that are activated in response to elevated temperatures and other stresses to help protect cells by producing heat-shock proteins.
Molecular Chaperones
Proteins that assist the conformational folding or unfolding and the assembly or disassembly of other macromolecular structures, without being part of these structures when they perform their biological functions.
Housekeeping Genes
These are genes that are constantly active in the cell to maintain basic functions and cellular metabolism.
Q5: A rigid, planar structure between at least
Q8: During muscle contraction<br>A)myosin pulls actin filaments toward
Q10: Anthrax toxin functions by altering levels of
Q10: The electrons used to convert an NDP
Q11: The reaction NADH <span
Q11: Which of the following amino acid residues
Q13: Which of the following scientists is now
Q15: Find the initial velocity for an
Q39: Determine the K<sub>M</sub> and V<sub>max</sub> from the
Q46: An important structural lipid found in nerve