Figure 9.7 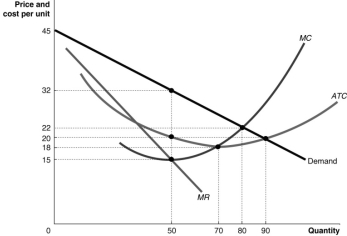
-Refer to Figure 9.7.Use the figure above to answer the following questions.
a.What is the profit-maximising quantity and what price will the monopolist charge?
b.What is the total revenue at the profit-maximising output level?
c.What is the total cost at the profit-maximising output level?
d.What is the profit?
e.What is the profit per unit (average profit)at the profit-maximising output level?
f.If this industry was organised as a perfectly competitive industry, what would be the profit-maximising price and quantity?
__________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Definitions:
Competitive Equilibrium
A market state where supply equals demand, and no economic actors have the incentive to change their behavior.
Demand Equals Supply
A market equilibrium condition where the quantity of a good or service demanded by consumers equals the quantity supplied by producers.
Numeraire
A unit of account or standard measure in economics used to compare the value of goods or services.
Pareto Optimal
Another term for Pareto Efficient; describes a situation where no one's condition can be improved without worsening someone else's condition.
Q4: Complete the following table.<br> <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4183/.jpg" alt="Complete
Q16: Suppose Argyle Sachs has to choose between
Q32: A patent<br>A) grants the creator of a
Q106: If the long-run average cost curve is
Q124: When a proposed merger between two companies
Q138: Refer to Figure 8-1. If the firm
Q157: Refer to Figure 7-13. The lines shown
Q177: How does the demand curve for an
Q183: Economies of scale will create a barrier
Q233: Compared to perfect competition, the consumer surplus