Account for the observation that ethyl alcohol, 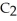
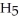 OH, dissolves readily in water but dimethyl ether, C
OH, dissolves readily in water but dimethyl ether, C 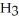 OC
OC 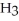 , which has the same number and kinds of atoms, does not.
, which has the same number and kinds of atoms, does not. 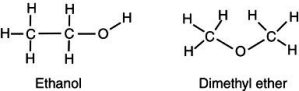
Definitions:
Competitors
Entities that offer similar products or services within the same market and vie for the same customer base.
Competitive Identity
The unique attributes and qualities that differentiate an organization or brand in the marketplace, influencing public perception and competitive positioning.
Core Benefit Proposition
The fundamental value or advantage that a product or service offers to customers, often serving as the primary reason for a consumer's purchase decision.
Direct Competitors
Businesses or entities that offer the same or very similar goods or services to the same customer or target market.
Q3: Which of the following statements best describes
Q4: For the following reaction, identify whether the
Q15: Which of the above images would best
Q23: How are pressure and the boiling point
Q28: Another interesting periodic trend is the density
Q37: How can a hydrogen atom, which has
Q101: If the relative mass of a hydrogen
Q117: Does the ozone pollution from automobiles help
Q128: How necessary is soap for removing salt
Q147: What is the sum of the atomic