Why is calcium fluoride, Ca 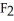 , a high melting point crystalline solid while tin (IV) chloride,
, a high melting point crystalline solid while tin (IV) chloride, 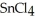 , is a volatile liquid?
, is a volatile liquid?
Definitions:
Managerial Accounting
The process of identifying, measuring, analyzing, and communicating financial information to managers for the pursuit of an organization's goals.
Product Costs
Expenses directly tied to the creation of products, including direct materials, direct labor, and factory overhead.
Factory Overhead Cost
All indirect costs associated with manufacturing, including utilities, maintenance, and manager salaries, but not direct materials or direct labor.
Manufacturing Process
The series of steps through which raw materials are transformed into a final product, involving both physical or chemical procedures.
Q21: How many molecules of sucrose are in
Q29: The strong nuclear force is very sensitive
Q44: Does the average distance that a neutron
Q47: Which of the following emits more radiation?<br>A)
Q77: It is relatively easy to pull an
Q82: Complete the following nuclear equation: <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6000/.jpg"
Q94: Which of the above liquids has the
Q124: Which covalent bond is more polar: a
Q126: Ice floats in room temperature water, but
Q137: In the following diagram, which of the