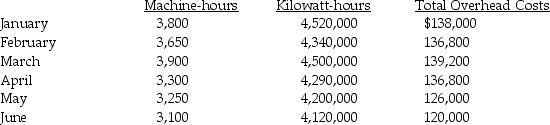
Tessmer Manufacturing Company produces inventory in a highly automated assembly plant in Windsor, Ontario.The automated system is in its first year of operation and management is still unsure of the best way to estimate the overhead costs of operations for budgetary purposes.For the first six months of operations, the following data were collected:
 Required:
Required:
a.Use the high-low method to determine the estimating cost function with machine-hours as the cost driver.
b.Use the high-low method to determine the estimating cost function with kilowatt-hours as the cost driver.
c.For July, the company ran the machines for 3,150 hours and used 4,180,000 kilowatt-hours of power.The overhead costs totaled $114,000.Which cost driver was the best predictor for July?
Definitions:
Sample Standard Deviation
A measure of the dispersion or variability of data points in a sample from the sample mean.
Significance Level
A threshold set by researchers before conducting an experiment to determine at what probability level results will be considered statistically significant, commonly set at 0.05 or 5%.
Type I Error
The incorrect rejection of a true null hypothesis, also known as a "false positive" finding.
Type II Error
The error made by failing to reject a false null hypothesis, often denoted as a false negative in hypothesis testing.
Q7: A paper company manufactures cardboard boxes.Because the
Q9: Which of the following is NOT one
Q50: The new cost analyst in your accounting
Q60: Central Dental Company manufactures dental chairs.Its most
Q63: Past costs that are unavoidable and unchangeable
Q69: When prices are set in a competitive
Q114: Life-cycle budgeting is necessary before a company
Q140: The key to a company's success is
Q182: Quantitative factors are always expressed in financial
Q218: The account analysis method estimates cost functions