AAA Metal Bearings produces two sizes of metal bearings (sold by the crate)-standard and heavy. The standard bearings require $200 of direct materials per unit (per crate)and the heavy bearings require $245 of direct materials per unit. The operation is mechanized and there is no direct labor. Previously AAA used a single plantwide allocation rate for manufacturing overhead, which was $1.55 per machine hour. Based on the single rate, gross profit data were as follows:
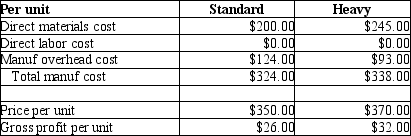 Although the data showed that the heavy bearings were more profitable than the standard bearings, the plant manager knew that the heavy bearings required much more processing in the metal fabrication phase than the standard bearings, and that this factor was not adequately reflected in the single allocation rate. He suspected that it was distorting the profit data. He suggested adopting an activity based costing approach.
Although the data showed that the heavy bearings were more profitable than the standard bearings, the plant manager knew that the heavy bearings required much more processing in the metal fabrication phase than the standard bearings, and that this factor was not adequately reflected in the single allocation rate. He suspected that it was distorting the profit data. He suggested adopting an activity based costing approach.
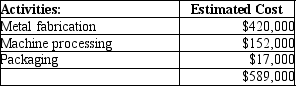
Working together, the engineers and accountants identified the following three manufacturing activities, and broke down the annual overhead costs as shown:
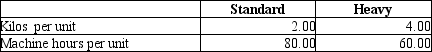
 Engineers believed that metal fabrication costs should be allocated by weight, and estimated that the plant processed 12,000 kilos of metal per year. Machine processing costs were correlated to machine hours, and the engineers estimated a total of 380,000 machine hours for the year. Packaging costs were the same for both types of products, and so they could be allocated simply by the number of units produced. The production plan provided for 4,000 units of standard and 1,000 units of heavy bearings to be produced during the year. Additional data on a per unit basis are as follows:
Engineers believed that metal fabrication costs should be allocated by weight, and estimated that the plant processed 12,000 kilos of metal per year. Machine processing costs were correlated to machine hours, and the engineers estimated a total of 380,000 machine hours for the year. Packaging costs were the same for both types of products, and so they could be allocated simply by the number of units produced. The production plan provided for 4,000 units of standard and 1,000 units of heavy bearings to be produced during the year. Additional data on a per unit basis are as follows:
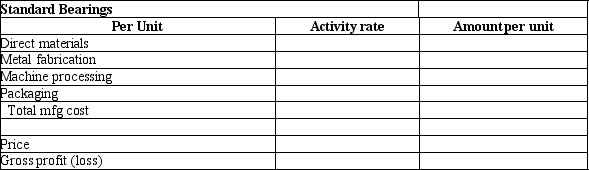
 Using the data above, please calculate activity rates. Then, following the ABC methodology, calculate the production cost and gross profit for one unit of heavy bearings, using the format below:
Using the data above, please calculate activity rates. Then, following the ABC methodology, calculate the production cost and gross profit for one unit of heavy bearings, using the format below:
Definitions:
Identity
A person’s sense of self, characterized by unique attributes, beliefs, and experiences that distinguish them from others.
Kohlberg
A psychologist best known for his theory of moral development, which proposes that moral reasoning develops in six stages through an individual's lifetime.
Moral Reasoning
The process of determining right or wrong in a given situation, based on ethical principles and moral values.
Homework
Tasks assigned to students by school teachers that are intended to be completed outside of class.
Q4: Fogelin Promotional Services uses a job order
Q26: Burr Hill golf course is planning for
Q39: The records at Smith and Jones Company
Q54: If you invest $1,000 at the end
Q76: Martin Manufacturers produces 3 models of industrial
Q101: Fixed costs divided by the contribution margin
Q107: Altina Company just finished job A40. It
Q133: Sullivan Company is considering the purchase of
Q138: Some companies use contribution margin rather than
Q152: Arabica Manufacturing Company uses a predetermined manufacturing