If testing the difference between two population proportions under independent sampling, you pool the sample proportions and compute  as
as  =
= 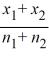 ________.
________.
Definitions:
Multiple Roles
Describes the situation of individuals who simultaneously engage in various social positions or responsibilities, such as being a parent, employee, and spouse, and the complexities that arise from managing these roles.
Spouse
A partner in marriage or a committed intimate relationship.
Parent
A caretaker of offspring in their own species; also involves the guidance, care, and emotional support of a child.
Worker
An individual engaged in a specific activity or employment, especially for wage or salary.
Q11: According to the recent report, scientists in
Q18: For a hypothesis test about the difference
Q44: A bank is trying to determine which
Q45: According to a recent survey, women chat
Q57: A 7,000-seat theater is interested in determining
Q58: A recent study from the University of
Q64: It is generally believed that no more
Q83: A doctor thinks he has found a
Q90: When testing the difference between two population
Q99: Find the value x for which<br>A) P(