The following are the competing hypotheses and the relevant summary statistics: Η0: 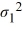 /
/ 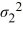 ≤ 1, ΗA:
≤ 1, ΗA: 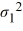 /
/ 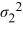 > 1.
> 1. 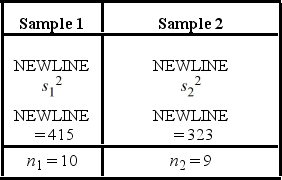 The p-value associated with the value of the test statistic is 0.3692. At the 5% significance level, which of the following conclusions is correct?
The p-value associated with the value of the test statistic is 0.3692. At the 5% significance level, which of the following conclusions is correct?
Definitions:
Opportunity Cost
The cost of forgoing the next best alternative when making a decision, representing the benefits one misses out on when choosing one option over another.
Point B
A specific position or location on a graph or diagram, used often in economic models to denote a particular outcome or situation.
Point A
A specific position or location often referenced in economic models or graphs to illustrate a particular scenario or outcome.
Opportunity Cost
The budgetary repercussion of passing on the subsequent top pick when decisions are taken.
Q27: Consider the following sample data: <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6618/.jpg"
Q54: Which of the following R functions is
Q64: Two students, Mary and Joanna, are in
Q71: A car dealership wants to estimate the
Q73: The following frequency distribution shows the monthly
Q87: The campaign manager for a candidate for
Q92: A manager at a local bank analyzed
Q97: Consider the following data: <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6618/.jpg" alt="Consider
Q134: Suppose the average math SAT score for
Q138: Consider the following sample regression equation <img