A sociologist studies the relationship between a district's average score on a standardized test for 10th-grade students (y), the average school expenditures per student (x1 in $1,000s), and an index of the socioeconomic status of the district (x2). The following model is estimated: Score = β0 + β1Expenditures + β2Index + ε. A portion of the regression results is shown in the accompanying table. 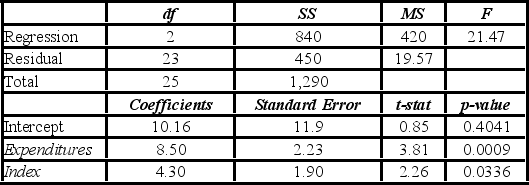 a. Predict a district's average test score if average expenditures are $4,500 and the district's social index is 8.
a. Predict a district's average test score if average expenditures are $4,500 and the district's social index is 8.
B) Interpret the slope coefficient for Expenditures.
C) Calculate the standard error of the estimate.
D) Calculate and interpret the coefficient of determination.
E) Calculate the adjusted R2.
Definitions:
Ethernet
Ethernet is a family of computer networking technologies commonly used in local area networks (LANs), metropolitan area networks (MANs), and wide area networks (WANs).
ISP
Internet Service Provider, a company that provides customers access to the Internet and related services.
Rural Areas
Regions located outside towns and cities, often characterized by lower population density and primarily agricultural land use.
Peer-To-Peer Processing
A distributed network architecture where each participant (peer) has equivalent capabilities and responsibilities, differing from traditional client-server models.
Q4: Based on quarterly data collected over the
Q5: Which of the following is not true
Q6: A card-dealing machine deals spades (1), hearts
Q20: It is believed that the sales volume
Q20: A researcher wants to understand how an
Q53: Consider the sample regression equation: <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6618/.jpg"
Q77: A career counselor wants to understand if
Q78: A model y = β<sub>0</sub> + β<sub>1</sub>x
Q81: A researcher with the Ministry of Transportation
Q90: Consider the partially completed two-way ANOVA (with