An analyst examines the effect that various variables have on crop yield. He estimates y = β0 + β1x1 + β2x2 + β3x3 + ε. where y is the average yield in bushels per acre, x1 is the amount of summer rainfall, x2 is the average daily use in machine hours of tractors on the farm, and x3 is the amount of fertilizer used per acre. The results of the regression are as follows: 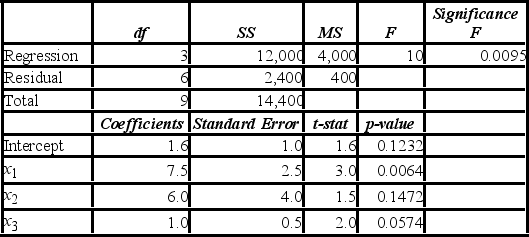 a. At the 10% significance level, are the explanatory variables jointly significant in explaining crop yield? Explain.
a. At the 10% significance level, are the explanatory variables jointly significant in explaining crop yield? Explain.
B) At the 10% significance level, is fertilizer significant in explaining crop yield? Explain.
C) At the 10% significance level, can you conclude that the slope coefficient attached to rainfall differs from 9? Explain.
Definitions:
Coastline Uplifted
The rise of landmasses relative to the sea level, often caused by tectonic activities such as earthquakes or isostatic adjustments, leading to changes in coastal landscapes.
Subsided
The process by which an area of land sinks to a lower level than the surrounding land area, often due to natural geological processes or the extraction of underground resources.
1964 Alaskan Earthquake
A powerful seismic event that struck Southcentral Alaska on March 27, 1964, also known as the Great Alaskan Earthquake, the second most powerful earthquake ever recorded.
Plate Tectonics
The scientific theory explaining the movement of the Earth's lithosphere through processes such as spreading, subduction, and collision, which results in the formation of mountains, earthquakes, and volcanoes.
Q19: The following table provides the price and
Q48: A researcher wants to understand how an
Q52: The airline industry defines "no-shows" as passengers
Q54: The following table shows the number of
Q57: An over-the-counter drug manufacturer wants to examine
Q82: The ANOVA test performed for determined that
Q83: For the log-log model ln(y) = β<sub>0</sub>
Q111: Consider the following simple linear regression model:
Q111: Variables employed in a regression model can
Q117: Consider the following regression results based on