To examine the differences between salaries of male and female middle managers of a large bank, 90 individuals were randomly selected, and two models were created with the following variables considered: Salary = the monthly salary (excluding fringe benefits and bonuses) ,
Educ = the number of years of education,
Exper = the number of months of experience,
Train = the number of weeks of training,
Gender = the gender of an individual; 1 for males, and 0 for females.
The Excel partial outputs corresponding to these models are available and shown below.
Model A: Salary = β0 + β1Educ + β2Exper + β3Train + β4Gender + ε  Model B: Salary = β0 + β1Educ + β2Exper + β3Gender + ε
Model B: Salary = β0 + β1Educ + β2Exper + β3Gender + ε 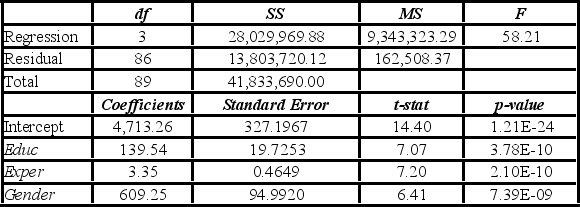 A group of female managers considers a discrimination lawsuit if on average their salaries could be statistically proven to be lower by more than $500 than the salaries of their male peers with the same level of education and experience. Using Model B, what is the conclusion of the appropriate test at 10% significance level?
A group of female managers considers a discrimination lawsuit if on average their salaries could be statistically proven to be lower by more than $500 than the salaries of their male peers with the same level of education and experience. Using Model B, what is the conclusion of the appropriate test at 10% significance level?
Definitions:
Cognitive Abnormal
Describes conditions or disorders that affect the way a person thinks, learns, and processes information, differing significantly from what is considered typical or normal.
Aggression
A range of behaviors intended to harm or intimidate others, stemming from biological, social, or psychological factors.
Temperament
Characteristic differences among individuals in emotional reactivity, self-regulation, and activity that influence reactions to the environment and are stable and appear early in life.
Biological Influence
Factors related to genetics, physiology, and physical health that affect an individual's behavior, mood, and cognitive functions.
Q28: The accompanying table shows the regression results
Q46: An energy analyst wants to test if
Q54: The Kruskal-Wallis test is always a _-tailed
Q68: An analyst examines the effect that various
Q68: Consider the model y = β<sub>0 </sub>+
Q74: Price indices are used to remove the
Q84: A cubic regression model is a polynomial
Q98: The following table provides the prices of
Q120: A call option loses intrinsic value when
Q138: Consider the following sample regression equation <img