A realtor wants to predict and compare the prices of homes in three neighboring locations. She considers the following linear models:
Model A: Price = β0 + β1 Size + β2 Age + ε
Model B: Price = β0 + β1 Size + β3 Loc1 + β4 Loc2 + ε
Model C: Price = β0 + β1 Size + β2 Age + β3 Loc1 + β4 Loc2 + ε
where,
Price = the price of a home (in $1,000s)
Size = the square footage (in sq. feet)
Loc1 = a dummy variable taking on 1 for Location 1, and 0 otherwise
Loc2 = a dummy variable taking on 1 for Location 2, and 0 otherwise
After collecting data on 52 sales and applying regression, her findings were summarized in the following table. 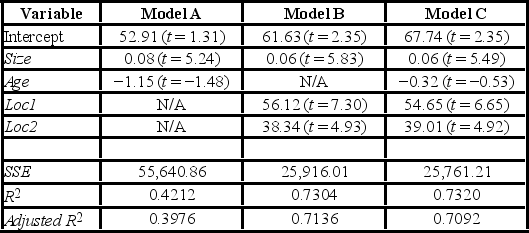 Note: The values of relevant test statistics are shown in parentheses below the estimated coefficients.
Note: The values of relevant test statistics are shown in parentheses below the estimated coefficients.
Using Model C, define the alternative hypothesis for testing the individual significance of Age.
Definitions:
Lodging
Accommodation in hotels, motels, or any other establishment that provides a place to stay for a short period.
Rational Choice
A theory in economics and sociology that suggests individuals choose the option that provides the highest level of satisfaction, assuming the availability of information and a clear preference set.
Opportunity Cost
The effect of spurning potential profits from various options by selecting a particular one.
Societal Choices
Decisions made by a society as a whole about the allocation of resources and priorities among different uses.
Q8: The fit of the regression equations <img
Q12: When a time series is analyzed by
Q17: In the quadratic trend model, y<sub>t</sub> =
Q25: For the logit model, the predicted values
Q38: Which of the following regression models does
Q54: Holding all else constant, call options with
Q72: When the forecasting method of seasonal dummy
Q108: A bank manager is interested in assigning
Q123: A linear trend can be estimated using
Q140: The clearinghouse 'novates' share option trading.