A realtor wants to predict and compare the prices of homes in three neighboring locations. She considers the following linear models:
Model A: Price = β0 + β1 Size + β2 Age + ε
Model B: Price = β0 + β1 Size + β3 Loc1 + β4 Loc2 + ε
Model C: Price = β0 + β1 Size + β2 Age + β3 Loc1 + β4 Loc2 + ε
where,
Price = the price of a home (in $1,000s)
Size = the square footage (in sq. feet)
Loc1 = a dummy variable taking on 1 for Location 1, and 0 otherwise
Loc2 = a dummy variable taking on 1 for Location 2, and 0 otherwise
After collecting data on 52 sales and applying regression, her findings were summarized in the following table. 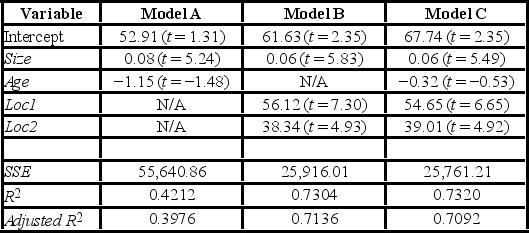 Note: The values of relevant test statistics are shown in parentheses below the estimated coefficients.
Note: The values of relevant test statistics are shown in parentheses below the estimated coefficients.
Which of these three models would you choose to make the predictions of the home prices?
Definitions:
Monument
A structure erected to commemorate persons or events of historical, cultural, or social significance.
Abu Simbel
An ancient temple complex in southern Egypt, built by Pharaoh Ramesses II, featuring monumental statues and intricate carvings.
Thebes
An ancient Egyptian city located along the Nile river, known for its wealth, art, and architectural sites like the Karnak Temple and the Valley of the Kings.
Old Kingdom
The period in ancient Egyptian history characterized by the construction of the pyramids, spanning from around 2686 to 2181 BCE.
Q5: An energy analyst wants to test if
Q12: Which of the following is the correct
Q19: Thirty employed single individuals were randomly selected
Q28: The accompanying table shows the regression results
Q41: An over-the-counter drug manufacturer wants to examine
Q53: The following table shows the value of
Q78: In the following diagram: <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4219/.jpg" alt="In
Q102: The following table includes the information about
Q113: Alex Aliyev is a primary school teacher.
Q115: Which of the following investors would be