To examine the differences between salaries of male and female middle managers of a large bank, 90 individuals were randomly selected, and two models were created with the following variables considered: Salary = the monthly salary (excluding fringe benefits and bonuses) ,
Educ = the number of years of education,
Exper = the number of months of experience,
Train = the number of weeks of training,
Gender = the gender of an individual; 1 for males, and 0 for females.
Excel partial outputs corresponding to these models are available and shown below.
Model A: Salary = β0 + β1Educ + β2Exper + β3Train + β4Gender + ε 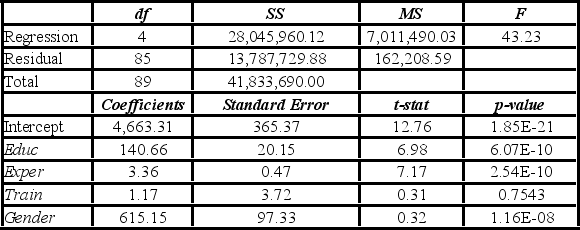 Model B: Salary = β0 + β1Educ + β2Exper + β3Gender + ε
Model B: Salary = β0 + β1Educ + β2Exper + β3Gender + ε 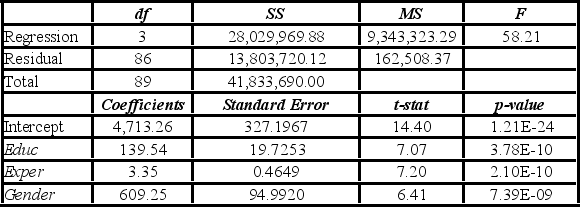 Assuming the same years of education and months of experience, what is the null hypothesis for testing whether the mean salary of males is greater than the mean salary of females using Model B?
Assuming the same years of education and months of experience, what is the null hypothesis for testing whether the mean salary of males is greater than the mean salary of females using Model B?
Definitions:
Technology Budgets
Allocations of financial resources dedicated to the acquisition, maintenance, and upgrade of technological tools and infrastructure in educational settings.
Educational Delivery
The methods and processes through which educational content is provided to learners.
Homework Calendars
Tools used by educators and students to organize and plan out homework assignments over a period, usually a month, to manage time effectively.
Differentiate
To identify or ascertain differences between two or more entities or concepts.
Q17: In the quadratic trend model, y<sub>t</sub> =
Q29: A farmer plants tomato seeds into four
Q36: The term multicollinearity refers to the condition
Q66: In forecasting methods, the mean square error
Q68: Given the following portion of regression results,
Q106: A market researcher is studying the spending
Q106: An admissions officer wants to examine the
Q111: It is believed that the sales volume
Q127: A researcher has developed the following regression
Q140: A sociologist examines the relationship between the