A realtor wants to predict and compare the prices of homes in three neighboring locations. She considers the following linear models:
Model A: Price = β0 + β1 Size + β2 Age + ε
Model B: Price = β0 + β1 Size + β3 Loc1 + β4 Loc2 + ε
Model C: Price = β0 + β1 Size + β2 Age + β3 Loc1 + β4 Loc2 + ε
where,
Price = the price of a home (in $1,000s)
Size = the square footage (in sq. feet)
Loc1 = a dummy variable taking on 1 for Location 1, and 0 otherwise
Loc2 = a dummy variable taking on 1 for Location 2, and 0 otherwise
After collecting data on 52 sales and applying regression, her findings were summarized in the following table. 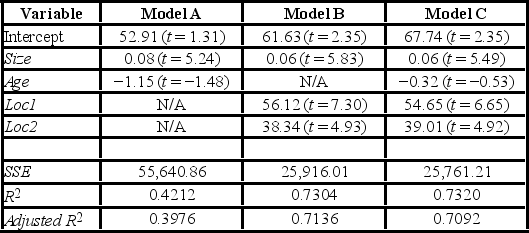 Note: The values of relevant test statistics are shown in parentheses below the estimated coefficients.
Note: The values of relevant test statistics are shown in parentheses below the estimated coefficients.
Using Model C, define the null hypothesis for testing the joint significance of the two dummy variables.
Definitions:
Accounts Receivable
Money owed to a company by its customers for goods or services that have been delivered or used but not yet paid for.
Net Sales
The amount of sales revenue remaining after deducting returns, allowances for damaged or missing goods, and discounts.
Income Statement
A financial statement that shows a company's revenues and expenses over a specific period of time, resulting in a net profit or loss.
Budgeted Amounts
Estimated financial figures planned for a certain period, including revenues and expenses.
Q3: A call option is equivalent to a
Q22: When the decomposition model, y<sub>t</sub> = T<sub>t</sub>
Q39: ASX options have as the contract item
Q41: Dealers and brokers both play a role
Q41: Typically, the sales volume declines with an
Q66: Three firms, X, Y, and Z, operate
Q90: A company that produces financial accounting software
Q94: If there are T observations to estimate
Q96: A researcher wants to examine how the
Q101: For the quadratic regression model <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6618/.jpg"