Two stationary point charges q1 and q2 are shown in the figure along with a sketch of some field lines representing the electric field produced by them. What can you deduce from the sketch? 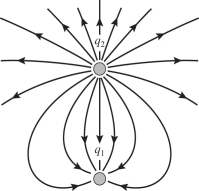
Definitions:
Full-Rectification
The conversion of AC (alternating current) to DC (direct current) using both halves of the input waveform, usually in power supply or electronic signal processing.
Rotor
The rotating part of an electrical or mechanical device, such as the part in an electric generator or motor which turns around a stationary part called a stator.
Stator
(1) A stationary element in a rotating component; (2) The stationary member of an alternator into which electrical current is induced by the rotor; (3) Intermediary in a torque converter torus located between the impeller and turbine; redirects oil from the turbine back to the impeller.
Rectifier
An electrical device that converts alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC), often used in power supply systems.
Q31: A 4.0-g string is 0.39 m long
Q33: In the circuit shown in the figure,
Q39: A 5.0-μF, a 14-μF, and a
Q74: An air-filled parallel-plate capacitor is constructed with
Q84: A lens of focal length 40 mm
Q101: A soap bubble film that is 106
Q103: Two isolated copper plates, each of area
Q124: Kirchhoff's loop rule is a statement of<br>A)
Q145: A 8.0-μF uncharged capacitor is connected in
Q149: A cell phone is placed 40 cm