The angle between vector 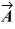 = 2.00
= 2.00  + 3.00
+ 3.00  and vector
and vector 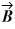 is
is 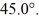 The scalar product of vectors
The scalar product of vectors 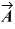 and
and 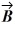 is 3.00.If the x component of vector
is 3.00.If the x component of vector 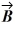 is positive,what is vector
is positive,what is vector 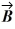 .
.
Definitions:
Monthly Profit
The net income earned by a business over the course of a month after all expenses have been subtracted from total revenue.
Unbounded Problem
A scenario in optimization where the solution can infinitely improve, meaning there are no constraints limiting the value of the objective function.
Objective
A goal or target that is aimed to be achieved, usually specific, measurable, and time-bound.
Without Bound
An expression indicating that there is no limit or boundary to a certain condition or value.
Q4: An airplane is flying at a speed
Q15: When a rigid body rotates about a
Q21: A uniform disk,a uniform hoop,and a uniform
Q30: A person is dragging a packing crate
Q34: You do 174 J of work while
Q47: Referring to Instruction 19-3,which pair(s)of observations has
Q67: Consider the following two bonds: a discount
Q86: You have the opportunity to invest at
Q98: Referring to Instruction 18-16,what is the value
Q117: By example,diagram,and/or verbal description,demonstrate how put options