On a hot summer day,the temperature is 40.0°C and the pressure is 1.01 × 105 Pa.Let us model the air as all nitrogen of molecular mass 28.0 g/mol having molecules of diameter 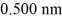 that are moving at their root-mean-square speed.Avogadro's number is
that are moving at their root-mean-square speed.Avogadro's number is 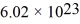 molecules/mol,the ideal gas constant is 8.31 J/mol • K,and the Boltzmann constant is
molecules/mol,the ideal gas constant is 8.31 J/mol • K,and the Boltzmann constant is 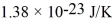 .Calculate reasonable estimates for
.Calculate reasonable estimates for
(a)the root-mean-square speed of the nitrogen molecules.
(b)the average distance a typical molecule travels between collisions.
(c)the average time a molecule travels between collisions,assuming that the molecules are moving at their root-mean-square speeds.
(d)the number of collisions an average molecule undergoes per second.
Definitions:
Standard Deviation Units
A measure of the amount of variation or dispersion of a set of values, indicating how much the individual values differ from the mean of the sample.
Normal Distribution
A normal distribution is a bell-shaped frequency distribution curve, where most of the occurrences take place around the central peak, and the probabilities of values further away from the mean taper off symmetrically.
Standard Deviation
Standard deviation is a statistical measure that quantifies the amount of variability or dispersion in a set of data values, indicating how much the individual data points differ from the mean of the data set.
Distribution
The arrangement of values of a variable showing their observed or theoretical frequency of occurrence.
Q8: Consider the circuit shown in the figure.Note
Q13: A thin cylindrical shell is released from
Q13: If you double the pressure on the
Q22: A Carnot refrigerator takes heat from water
Q23: A 1.0 m long piece of coaxial
Q31: A 1.5-kg mass attached to an ideal
Q34: An ideal gas is compressed in a
Q49: It is necessary to determine the specific
Q62: A 648-g empty iron kettle is put
Q65: A 1.30-m long gas column that is