An electron is in an infinite square well (a box) that is 2.0 nm wide.The electron makes a transition from the 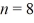 to the
to the 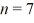 state,what is the wavelength of the emitted photon?
state,what is the wavelength of the emitted photon? 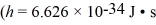 ,mel = 9.11 × 10-31 kg,1 eV = 1.60 × 10-19)
,mel = 9.11 × 10-31 kg,1 eV = 1.60 × 10-19)
Definitions:
Subpubic Angle
The angle formed below the pubic symphysis, varying in width between sexes and used in determining skeletal sex.
Thickness
Thickness refers to the measurement of an object from one surface to its opposite surface.
Shape of Pelvic Inlet
Describes the contour or opening at the top of the pelvis, which can vary, influencing childbirth and pelvic anatomy studies.
Calcaneus
The calcaneus, or heel bone, is a large bone in the foot that forms the foundation of the rear part of the foot and supports body weight.
Q4: Sample information with an efficiency rating of
Q10: A single slit forms a diffraction pattern
Q10: A feasible solution is one that satisfies
Q12: What is the occupancy probability at an
Q13: A capacitor is charging in a simple
Q19: The eyepiece of a compound microscope has
Q25: Consider a Poisson probability distribution in a
Q27: a)In an ac circuit,if the peak value
Q28: Heavier stable nuclei tend to have<br>A) half
Q31: Suppose you were to try to create