An alkali metal atom is in the ground state.The orbital angular momentum equals zero and the spin angular momentum is entirely due to the single valence electron.A magnetic field is applied that splits the ground state energy level into two levels,65 μeV apart.A photon,absorbed by the atom,induces a transition between the two levels.What is the wavelength of the photon? (c = 3.00 × 108 m/s,h = 6.626 × 10-34 J • s,Bohr magneton = μB = 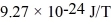 ,
, 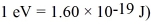
Definitions:
Bootstrap
A statistical method used for estimating the sampling distribution of an estimator by sampling with replacement from the original data.
Bootstrap Sample
A resampling technique used in statistics where repeated samples are drawn with replacement from an original dataset.
Replacement
Replacement is the act of substituting or exchanging something with a new or different version.
Original Sample
The initial group of participants or observations collected for analysis or experimentation before any manipulation or selection takes place.
Q13: Global Airlines operates two types of jet
Q18: A diffraction grating has rulings of 890
Q18: The energy of an electron state has
Q21: A nonrelativistic proton is confined to a
Q22: In an electromagnetic wave,the electric and magnetic
Q23: If the intensity of an electromagnetic wave
Q28: Which of the following statements about a
Q32: Time series methods<br>A)discover a pattern in historical
Q37: If two electrons in the same atom
Q43: EVPI is always greater than or equal