Super Cola is also considering the introduction of a root beer drink.The company feels that the probability that the product will be a success is .6.The payoff table is as follows:
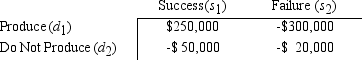 The company has a choice of two research firms to obtain information for this product.Stanton Marketing has market indicators,I1 and I2 for which P(I1SYMBOL 189 \f "Symbol"s1)= .7 and P(I1SYMBOL 189 \f "Symbol"s2)= .4.New World Marketing has indicators J1 and J2 for which P(J1SYMBOL 189 \f "Symbol"s1)= .6 and P(J1SYMBOL 189 \f "Symbol"s2)= .3.
The company has a choice of two research firms to obtain information for this product.Stanton Marketing has market indicators,I1 and I2 for which P(I1SYMBOL 189 \f "Symbol"s1)= .7 and P(I1SYMBOL 189 \f "Symbol"s2)= .4.New World Marketing has indicators J1 and J2 for which P(J1SYMBOL 189 \f "Symbol"s1)= .6 and P(J1SYMBOL 189 \f "Symbol"s2)= .3.
a.What is the optimal decision if neither firm is used? Over what probability of success range is this decision optimal?
b.What is the EVPI?
c.Find the EVSIs and efficiencies for Stanton and New World.
d.If both firms charge $5,000,which firm should be hired?
e.If Stanton charges $10,000 and New World charges $4,000,which firm should Super Cola hire? Why?
Definitions:
Developed
Refers to countries or regions that have a high level of industrialization, a strong economy, and generally high living standards.
Felt Conflict
The personal perception or experience of being in conflict, which can differ from the actual existence of a conflict situation.
Discomfort
A feeling of unease or mild pain, often a signal that something may need attention or change.
Motivates
Acts or factors that stimulate enthusiasm and energy in someone to do something.
Q6: Consider two different isotopes of the same
Q9: In a transportation problem with total supply
Q12: For a multiplicative time series model,the sum
Q21: Frederick Taylor is credited with forming the
Q23: If P<sub>ij</sub> = the production of product
Q31: A 70-kg laboratory technician absorbs 2.9 mJ
Q33: A nonrelativistic electron has a kinetic energy
Q43: An assumption in the economic production lot
Q44: In the vicinity of what frequency does
Q55: The difference between the transportation and assignment