An airline reservation system first asks customers whether they want to schedule a domestic or an international flight.Sixty-five percent of the reservations are for domestic flights.The time distribution of advance sales is also important,and it is given below.
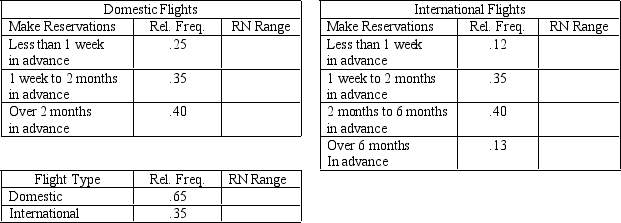
a.Place the appropriate random number ranges in the tables above.
b.Set up and perform a simulation for three customers.Determine whether they want a domestic or international flight,and how far in advance the reservation is being made.Use random numbers from this list: .632 .715 .998 .671 .744 .021
Definitions:
Positive Transfer
The beneficial effect of past learning on the acquisition of new skills or knowledge, where previous experiences facilitate performance on a new task.
Déjà Vu
That eerie sense that “I’ve experienced this before.” Cues from the current situation may unconsciously trigger retrieval of an earlier experience.
Misinformation Effect
A cognitive phenomenon where a person's recall of an event becomes less accurate due to the introduction of misleading information.
Retroactive Interference
A memory phenomenon where new information disrupts the recall of older information.
Q1: A forecast cell refers to a random
Q6: The triangular distribution has a fixed upper
Q16: RSPE can not handle constraints in a
Q17: Arcs in a transshipment problem<br>A)must connect every
Q33: Inventory position is defined as<br>A)the amount of
Q33: 52 <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2459/.jpg" alt="52 A)3
Q35: The probability that the system is
Q48: There are four activities on the critical
Q52: Whenever total supply is less than total
Q54: Find the maximal flow from node 1