Consider the following convex programming problem.Maximize f(x)= 10x1 - 2 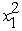 -
- 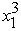 + 8x2 -
+ 8x2 - 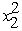 ,subject to x1 + x2 ≤ 2 and x1 ≥ 0,x2 ≥ 0.(a)Use the KKT conditions to demonstrate that (x1,x2)= (1,1)is not an optimal solution.
,subject to x1 + x2 ≤ 2 and x1 ≥ 0,x2 ≥ 0.(a)Use the KKT conditions to demonstrate that (x1,x2)= (1,1)is not an optimal solution.
(b)Use the KKT conditions to derive an optimal solution.
Definitions:
Plant Virus
Infectious agents that can replicate only inside the living cells of plants, causing various diseases.
Corn Crops
Corn crops, or maize, are cereal grain plants grown for their edible seeds, significant as a staple food resource globally and also used for animal feed, biofuel, and other products.
Comparative Genomics
The study and comparison of genomes from different species to understand genetic similarities, differences, and evolutionary relationships.
Genomes
A genome comprises all the genetic material in an organism, representing the entire set of DNA, including all of its genes and non-coding sequences.
Q2: According to the absorption approach,an increase in
Q6: Cool Power produces air conditioning units for
Q17: What are the three other main activities
Q30: Since the introduction of the computer,there has
Q47: Which of the following is an example
Q54: Gold is currently the most widely used
Q54: The _ entity is used to collect
Q61: There are several steps in the data
Q77: What is a disadvantage of an organization's
Q78: What is the basic building block of