Vita-Heath Company manufactures three different types of vitamins: vitamin C,vitamin B,and vitamin D.The company uses four operations to manufacture the vitamins: mixing,tabletting,encapsulating,and bottling.Vitamins C and B are produced in tablet form (in the tabletting department)and vitamin D is produced in capsule form (in the encapsulating department).Each bottle contains 80 vitamins,regardless of the product.
Conversion costs are applied based on the number of bottles in the tabletting and encapsulating departments.Conversion costs are applied based on direct labour hours in the mixing department.It takes two minutes to mix ingredients for a 80-unit bottle for each product.Conversion costs are applied based on machine hours in the bottling department.It takes one-tenth of a minute of machine time to fill a 80-unit bottle,regardless of product.
Vita-Health Company uses operation costing.
The company is planning to complete one batch of each type of vitamin in March.The budgeted number of bottles and expected direct material cost for each type of vitamin is as follows:
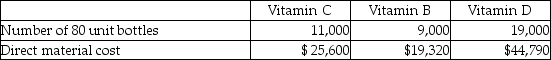
The budgeted conversion costs for March are as follows:
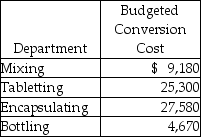
Required:
1.Calculate the conversion cost rates for each department.
2.Calculate the budgeted cost of goods manufactured for vitamin C,vitamin B,and vitamin D for the month of March.
3.Calculate the cost per 80-unit bottle for each type of vitamin for the month of July.
Definitions:
Nuclear Receptor Model
A framework for understanding how certain receptor proteins within cell nuclei mediate the effects of lipophilic hormones, vitamins, and other ligands.
Receptor Molecule
A protein on the surface of a cell that binds to specific molecules, triggering a response in the cell.
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid, a molecule that carries the genetic instructions used in the growth, development, functioning, and reproduction of all known living organisms and many viruses.
Nuclear Receptor Model
A conceptual framework explaining how specific receptors within cell nuclei regulate gene expression in response to hormones and other molecules.
Q1: The fixed and variable costs allocated to
Q20: What is the static budget variance (contribution
Q21: What is the effect of the following
Q33: Each division manager for a paint manufacturer
Q43: The costs of abnormal spoilage are<br>A)locked-in in
Q83: Which method allocates joint costs on the
Q96: Which of the following journal entries would
Q98: The products of a joint production process
Q99: The selection of a joint cost allocation
Q137: The management accountant aids in MRP by<br>A)doing