Table 2-6
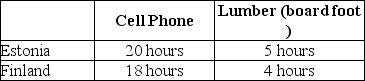
-Refer to Table 2-6.This table shows the number of labor hours required to produce a cell phone and a board foot of lumber in Estonia and Finland.
a.If each country has a total of 3,600 labor hours to devote to the production of the two goods,draw the production possibilities frontier for each country.Put "Cell Phone" on the horizontal axis and "Lumber" on the vertical axis.Be sure to identify the intercept values on your graphs.
b.Suppose each country allocates 55% its labor hours to lumber production and 45% to the production of cell phones.Complete Table 2-7 below to show each country's output of the two products.
Table 2-7: Production and Consumption with no Trade
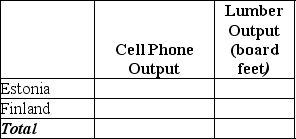 c.If the two countries do not trade and consume whatever they produce,identify the current production and consumption point for each country on their respective production possibilities frontiers.Label Estonia's consumption point "E" and Finland's consumption point,"F."
c.If the two countries do not trade and consume whatever they produce,identify the current production and consumption point for each country on their respective production possibilities frontiers.Label Estonia's consumption point "E" and Finland's consumption point,"F."
d.Suppose the two countries specialize and trade.Who should produce cell phones and who should produce lumber? Explain your answer.
e.Complete Table 2-8 below to show each country's output with specialization.
Table 2-8: Output with Specialization
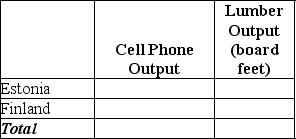 f.Did specialization increase the combined output for the two countries without any increase in resources? If so,by how much?
f.Did specialization increase the combined output for the two countries without any increase in resources? If so,by how much?
g.Suppose Estonia and Finland agree to trade so that in exchange for 400 board feet of lumber,the exporter of lumber receives 90 cell phones.Complete Table 2-9 below to show each country's consumption bundle after trade.
Table 2-9: Consumption with Trade
 h.Show the consumption points after trade on each country's production possibilities frontier.Label these points "X" for Estonia and "Y" for Finland.
h.Show the consumption points after trade on each country's production possibilities frontier.Label these points "X" for Estonia and "Y" for Finland.
i.Has trade made the two countries better off? Explain your answer.
Definitions:
Conductors
Materials that allow the flow of electric current through them, often used in electrical wiring and components.
Insulators
Materials or objects that do not easily conduct electricity, used to prevent unwanted flow of current.
Electromotive Force
The energy supplied per charge by a source of electrical energy, such as a battery or generator, measured in volts.
Volts
The unit of measurement for electric potential difference or electromotive force, central to understanding electric circuits.
Q19: Suppose there is some unemployment in the
Q28: A tax on interest earned from saving
Q29: Many firms use technology to gather information
Q60: If a monopolist practices perfect price discrimination,<br>A)the
Q65: If a vineyard wants to raise funds
Q74: You are given the following market data
Q77: Which of the following factors has significantly
Q80: Refer to Table 16-1.Suppose Julie's marginal cost
Q92: Refer to Figure 3-2.A technological advancement would
Q97: Goods that are excludable but not rival