Use the following information to answer the question(s) below..
Pelga Company routinely receives goods from its 80%-owned subsidiary,Swede Corporation.In 2011,Swede sold merchandise that cost $80,000 to Pelga for $100,000.Half of this merchandise remained in Pelga's December 31,2011 inventory.This inventory was sold in 2012.During 2012,Swede sold merchandise that cost $160,000 to Pelga for $200,000.$62,500 of the 2012 merchandise inventory remained in Pelga's December 31,2012 inventory.Selected income statement information for the two affiliates for the year 2012 was as follows:
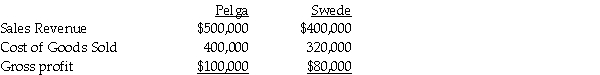
-What amount of unrealized profit did Pelga Company have at the end of 2012?
Definitions:
Finite Capacity Scheduling
A method for planning and controlling production where the limited availability of resources (machines, labor, etc.) is taken into account.
Instantaneous Changes
Rapid alterations in a system or process that occur in a nearly zero time frame, often used in physics to describe acceleration or in finance for stock price movements.
Rule-Based Scheduling
A method of organizing tasks or operations based on a set of predetermined rules to optimize performance or resource allocation.
Critical Ratio Sequencing
A prioritizing technique used in production scheduling where jobs are sequenced based on the ratio of the remaining time to due date to the remaining work.
Q4: For each of the 12 accounts listed
Q4: When actual inflation is less than expected
Q8: The Justin, Kyle, and Lulu partnership was
Q16: Which statement is correct in describing the
Q21: Under the provisions of FASB Statement No.141R,
Q26: On January 1, 2011, Adam Corporation purchased
Q33: Sally Corporation's stockholders' equity on December 31,
Q39: With respect to the bond purchase, the
Q44: Refer to Table 9-17.Looking at the table
Q156: In the circular flow model,the value of