The below figure shows the various combinations of the goods X and Y that yield different levels of utility.Figure 7.3
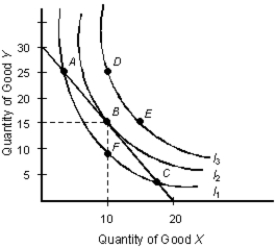
-A consumer is in equilibrium when the slope of his or her indifference curve is equal to his or her budget constraint.
Definitions:
Deadweight Loss
The drop in economic efficiency due to the inability or failure of a good or service to reach its equilibrium state.
Government Revenue
The total income received by the government from taxes, fees, and non-tax sources like government-owned enterprises and foreign aid.
Tax Rate
The share of an individual's or corporation's income that is subject to taxation.
Deadweight Loss
A loss in total economic welfare that occurs when the free market equilibrium for a good or a service is not achieved, typically due to taxes, subsidies, or market controls.
Q28: In long-run equilibrium, the monopolistically competitive firm:<br>A)will
Q37: If a monopolistically competitive industry is in
Q45: The long-run average-total-cost curve connects the lowest
Q45: Cross-price elasticity is represented by the formula
Q53: Which of the following is true of
Q57: A firm enjoys a positive economic profit
Q77: Which of the following will most likely
Q94: In the short run, if the marginal
Q103: If a monopolist is producing at a
Q135: Refer to Figure 10.2. If the marginal-revenue