The figure given below shows the revenue and cost curves of a perfectly competitive firm.Figure 10.2
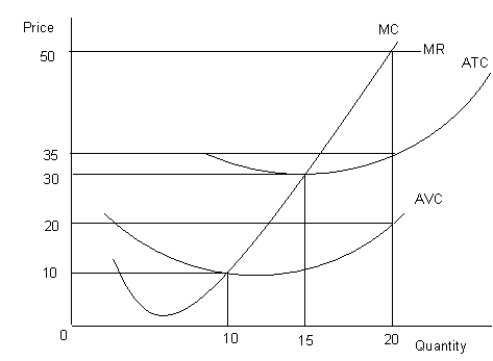 MC: Marginal cost curve
MC: Marginal cost curve
MR: Marginal revenue curve
ATC: Average-total-cost curve
AVC: Average-variable-cost curve
-Refer to Figure 10.2. Compute the profit earned by the firm at the profit-maximizing level of output.
Definitions:
Physical Substances
Materials or matter with mass and volume; physical substances include solids, liquids, and gases.
Real Property
Land and anything permanently attached to it, such as buildings or structures.
Personal Property
Tangible or intangible assets that are not real estate, such as vehicles, stocks, or intellectual property.
Personal Property
Items owned by an individual or entity that are movable and not fixed to one location, unlike real estate.
Q6: When a firm incurs negative economic profit,
Q13: In the long run, if the output
Q16: An "all you can eat" restaurant illustrates
Q44: Perfect price discrimination occurs when:<br>A)each customer is
Q67: A monopoly is a market model in
Q70: If a firm experiences economies of scale
Q81: In Table 8.5, what is the total
Q88: At long-run equilibrium of a perfectly competitive
Q94: A positive economic profit signals that the
Q121: A monopolist faces the least price-elastic demand