The figure given below shows the revenue and cost curves of a perfectly competitive firm.Figure 10.5
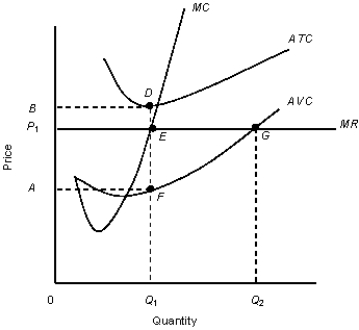 MC: Marginal cost curve
MC: Marginal cost curve
MR: Marginal revenue curve.ATC: Average-total-cost curve
AVC: Average-variable-cost curve
-An individual perfectly competitive firm's supply curve is its:
Definitions:
Business
An organizational entity that provides goods or services to consumers in exchange for monetary compensation.
Innovation
The introduction of new ideas, products, services, or processes, driving progress and offering competitive advantages in the business world.
Business Growth
The process of increasing the size, output, or market reach of a business, typically measured through sales, profits, or market share.
Self-Employment
A state of working for oneself rather than being employed by an employer, often leading to the operation of one's own business.
Q10: Each firm under monopolistic competition produces a
Q19: Refer to Figure 14.1. If the regulatory
Q32: If a firm doubles its resources and
Q36: Problems of moral hazard and adverse selection
Q36: Total utility is determined by:<br>A)multiplying the quantity
Q57: Consider the perfectly competitive firm described in
Q61: The demand curve for labor indicates that:<br>A)as
Q84: Short run refers to a period of
Q91: With expansion in the level of output,
Q97: Which of the following is true of