The figure given below shows the revenue and cost curves of a perfectly competitive firm.Figure 10.5
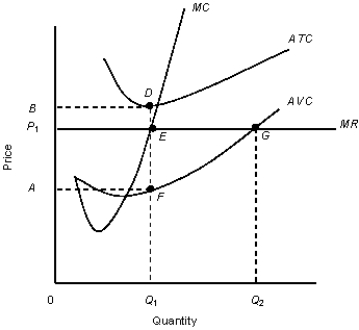 MC: Marginal cost curve
MC: Marginal cost curve
MR: Marginal revenue curve.ATC: Average-total-cost curve
AVC: Average-variable-cost curve
-A perfectly competitive firm's supply curve is the portion of the:
Definitions:
Accounts Payable
Financial obligations or debts that a company owes to its suppliers or creditors for goods and services received but not yet paid for.
Owners' Equity
Represents the residual interest in the assets of an entity after deducting liabilities, often referred to as shareholder equity.
Ending Inventory
Represents the final stock of goods available for sale by a firm at the close of an accounting period.
Beginning Inventory
The value of a company’s inventory at the start of an accounting period, carried over from the end of the previous period.
Q1: The judicial doctrine, being a monopoly or
Q7: If a firm is able to collect
Q17: Other things being equal, if there is
Q17: The marginal revenue curve of a firm
Q18: The free rider problem occurs because:<br>A)it is
Q90: The marginal fixed cost of a firm:<br>A)is
Q98: The long-run equilibrium price-output combination for a
Q99: Which of the following statements characterizes perfect
Q110: Accountants do not often report economic profits
Q117: Under price discrimination, a monopolist equates the